EVENTS
Read Articles
View All

Monsoon Bets: Unraveling the History of Rain Gambling in India
Rain gambling, or "Barsat ka Satta", originated in Rajasthan, where the Marwari community, facing perennial water scarcity, speculated on monsoon patterns. It spread to Calcutta (now known as Kolkata) in the 1800s, faced British opposition in Bombay (now known as Mumbai), and led to a court victory for Marwari rain gamblers. Despite protests, legislative amendments caused its decline and eventual ban in Calcutta by 1900. This unique chapter in gambling history reflects human adaptability amid monsoon unpredictability, serving as a nostalgic reminder of India's early weather derivatives.

Setting up of Limited Purpose Clearing Corporation (LPCC) by Asset Management Companies (AMCs) of Mutual Funds
Limited Purpose Clearing Corporation (LPCC) has been set up for the purpose of clearing and settlement of corporate bond repo transactions and to develop an active repo market. Accordingly, SEBI vide circular dated February 02, 2022 pave the way for establishment of LPCC by AMCs of Mutual Funds. The LPCCs are expected to help improve liquidity in the underlying corporate bond market.

Recognition of AMC Repo Clearing Limited (ARCL)
Limited Purpose Clearing Corporation (LPCC) has been set up for the purpose of clearing and settlement of corporate bond repo transactions and to develop an active repo market, SEBI Board, during September 2020, permitted the setting up of a Limited Purpose Clearing Corporation (LPCC). Accordingly, SEBI, vide circular dated February 02, 2022, pave the way for establishment of LPCC by AMCs of Mutual Funds. The LPCCs are expected to help improve liquidity in the underlying corporate bond market.

SEBI launches mobile application for lodging investor grievances
To improve the ease of doing business and to offer ease and convenience for investors to lodge their complaints, SEBI launched “SEBI SCORES” mobile application. SEBI SCORES, which is available on both iOS and Android platforms, will help investors access SCORES at the convenience of a smart phone.

Introduction of Investor Service Centres of Stock Exchanges
SEBI, vide circular December 03, 1997, advised all stock exchanges to open or maintain at least one Investor Service Centre (ISC) for the benefit of the investors. Such centres are required to, inter alia, provide counselling services and certain basic minimum facilities to the investors. The major stock exchanges were allowed to open as many ISCs as required. Considering significant developments in the securities market, including technological advancements, the provisions related to ISC (Investor Service Centers) of stock exchanges were reviewed. To enhance outreach to investors nationwide, stock exchanges were advised to utilize existing ISCs at various locations and were further instructed to open additional ISCs as necessary, in accordance with SEBI's specifications. The minimum basic facilities to be provided at each ISC were also specified.

Review of the provisions related to ISCs of stock exchanges
SEBI, vide circular dated December 03, 1997, advised all stock exchanges to open or maintain at least one Investor Service Centre (ISC) for the benefit of the investors. Such centres are required to, inter alia, provide counselling services and provide certain basic minimum facilities to the investors. The major stock exchanges were allowed to open as many ISCs as required. Considering significant developments in the securities market, including technological advancements, the provisions related to ISC (Investor Service Centers) of stock exchanges were reviewed. To enhance outreach to investors nationwide, stock exchanges were advised to utilize existing ISCs at various locations and were further instructed to open additional ISCs as necessary, in accordance with SEBI's specifications. The minimum basic facilities to be provided at each ISC were also specified.

Exit Policy for Stock Exchanges
SEBI took several policy initiatives with the objective of facilitating the exit process for non-operational stock exchanges.

Cotton Boom and Bust: The Legacy of India's First Stock Market Crash (Share Mania of 1861-1865)
“… 50 million sterling, if not more, of real wealth had been allowed to disappear like the baseless fabric of a vision, and how on the debris of such fabric the Bombay (now known as Mumbai) of today was re-built…”- DE Wacha, A Financial Chapter in the History of Bombay City. The American Civil War, which took place from 1861 to 1865, had a profound impact on global cotton supplies. Amidst the crisis, India emerged as a crucial alternative source of cotton for the textile mills of Europe. The Bombay Presidency, in particular, played a pivotal role in supplying cotton to meet this growing demand.
 on Stock Exchanges.jpg)
Impact of Bank Failures on Indian Stock Exchanges: A Case of ‘The Native Share and Stockbrokers’ Association’ (1913-1918)
The history of bank failures dates back to a few centuries but recorded ones are as far back as 17th century. In the early 20th century, the world's financial landscape underwent significant transformation. As nations braced themselves for the impending chaos of World War I, India's economy had to confront multiple challenges. One of the most significant economic events during this period was the series of domestic bank failures between 1913 and 1921, which left an indelible mark on Indian stock exchanges. A notable case during this period was that of a prominent member of the Native Share and Stock Brokers Association (earlier known as Bombay Stock Exchange and now BSE), Mr. Jahangir Byramji, who had a substantial holding in Manekji Petit Mill shares, was adjudicated as an insolvent.

Impact of Great Depression on Indian Stock Market, 1929
The Great Depression was the deepest and longest economic downturn of the 20th century that affected most of the major economies of the world. India, being a colonial export-oriented economy, was also adversely impacted by the Great Depression, primarily due to a crash in commodity prices in domestic and international markets. Further, stocks plummeted on major Indian exchanges, taking cues from global turmoil. However, by 1932, normalcy was restored in international trade and manufacturing activity and there was a sizable recovery in India as well. The article delves into the events leading to the Wall Street crash of 1929, the subsequent global economic depression, and the impact of these events on the Indian economy.
Watch Videos
View All

“Validated UPI Handles” and “SEBI Check” for secure investor payments
These two rollouts of “[at]valid Handle” and “SEBI Check” are expected to significantly enhance investor protection by curbing fraudulent money collections by unregistered entities.

Unified Distilled File Formats - UDiFF
SEBI promotes standardised reporting, savings of over Rs. 200 crore over 5 years, 90 percent reduction in reporting requirements for Brokers or Members, lower cost of entry for new fintech.
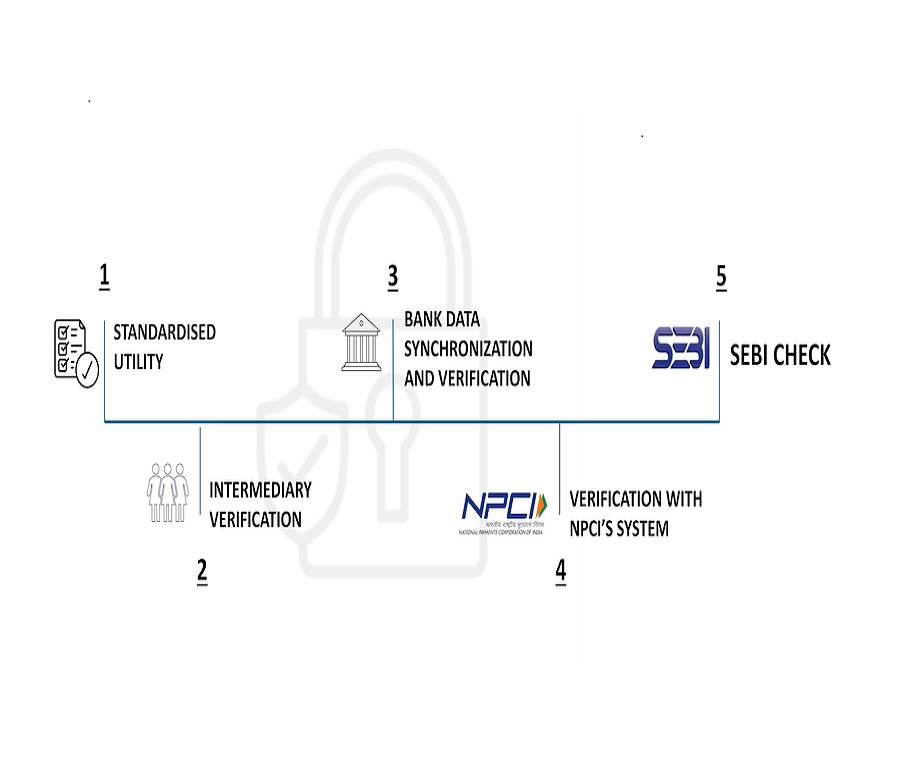
SEBI Introduced Validated UPI Handles and SEBI Check
SEBI announced a significant initiative to enhance investor protection and combat unauthorized money collection in the securities market. Effective October 1, 2025, SEBI will introduce a structured and validated UPI address mechanism, featuring the exclusive valid handle, for all SEBI-registered investor-facing intermediaries.
View Images
View All

SEBI clears first ever exchange traded fund
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has won the last legal battle over its decision to levy registration fees on stockbrokers on the basis of their turnover in the five-year period before the grant of registration. The Supreme Court dismissed the petition filed by the BSE Brokers' Forum challenging the fee and upheld SEBI's decision.

Govt gives SEBI an overhaul, more teeth
The Government of India, decided to empower the stock market regulator, SEBI, by giving it more teeth for investigation, including power of search and seizure. The decision was made due the episodes of market misconduct which showed the limitations of SEBI Act.
.png)
Dutch East India Company Bond, dated 7th November, 1623
‘Early Trading Companies’ Two pioneering trading companies, the Dutch East India Company and the British East India Company, hold an esteemed place in the annals of financial history. In 1602, the Dutch East India Company, established with exclusive rights to East Indies trade, initiated a momentous event—the world's first Initial Public Offering (IPO). This ground breaking offering heralded the birth of stock exchange trading, setting in motion a transformation in global commerce and investment. The British East India Company, founded on December 31, 1600, played a monumental role in the history of trade. Its joint stock shares were actively traded in London, signifying a burgeoning capital market. Notably, this enterprise consistently paid dividends to its investors, exemplifying reliability over centuries until its dissolution in 1874. In parallel, early debt instruments issued by the English East India Company, a predecessor to its British counterpart, demonstrated ingenuity in raising capital for ambitious ventures. These innovations in finance pushed the boundaries of what was conceivable in the realm of commerce. Together, these historical facts epitomize the genesis of modern financial systems. From the inaugural Dutch IPO, symbolizing the birth of stock exchange trading, to the British East India Company's unwavering dividends and inventive debt instruments, these companies laid the foundation for the contemporary financial markets we know today.

SC upholds SEBI fee on stockbrokers
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has issued show-case notices to the top brass of the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE) for their failure to detect and check price manipulation in three scripts, in its notice dated February 10, SEBI asked to explain lapses in detecting the abnormalities in price and volume in the scrips-Sterile Industries, BPL Ltd and Videocon Industries.

SEBI becomes members of IOSCO w.e.f. September 18, 1989
The Securities and Exchange Board of India has become a member of the Montreal-based International Organisation of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) with effect from September 18, 1989. This was the first time that India has been represented at this important international organisation.

SEBI orders compulsory demat trading in 10 scrips
The Securities Exchange Board of India has ordered compulsory settlement of traders in ten specified scrips in dematerialised form for institutional as well as other investor from January 4, 1999.

Commencement of settlement at NSDL
The electronic settlement of scrips in the National Securities Depository Ltd. which went live recently to commence this week (December 26, 1996)

NSDL introduction finally ushers in paperless trading
The launch of the National Securities Depository Limited has set in motion the most significant piece of reform in the country’s capital market. The depository will bring in paperless trading in shares and other securities, a feature now central to any mature securities market.

Mixed reaction to badla ban proposal. BSE Index dipped, 1993
The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) sensitive index dipped 86.99 points following reports in Times of India newspaper that the Securities and Exchange Board of India was considering the abolition of forward trading on all markets.

Pune bourse board superseded
The Securities and Exchange Board of India superseded the governing board of the Pune Stock Exchange for six months and appointed an administrator in its place. This is the first time the regulator has taken such stringent action on any stock exchange in the country.
