Brief Introduction of Commodity Markets
Commodity Derivatives Market in India
In India, organized trading in commodity derivatives started in India in 1875 by the Bombay Cotton Trade Association Limited with cotton as the underlying commodity. Subsequently, many other commodity derivatives trading centres emerged across the country.
Today, the Commodity derivatives trading in Indian exchanges has reached a sophisticated level. The exchanges offer electronic trading platforms for buyers and sellers to manage their price risks better and to improve the marketing of their physical products. Presently, the commodity derivatives are traded at four exchanges, namely, Multi Commodity Exchange (MCX), National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange, (NCDEX), BSE (formerly known as, Bombay Stock Exchange), and National Stock Exchange of India Ltd. (NSE).
Consequent to the merger of Forward Market Commission (FMC) with the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), the regulatory oversite of this segment is with SEBI.
At present, out of 92 commodities or their variants notified by Government for derivatives trading, the contracts are available for following commodities:
- Bullion (Precious metals): Gold and Silver
- Base (Industrial) Metals: Aluminium, Copper, Nickel, Zinc, Steel, Lead
- Energy: Crude oil and natural
- Agriculture: Corn, soybeans, wheat, rice, cocoa, coffee, cotton, and sugar are examples of recent agricultural commodities.
Product of Commodity Derivatives Markets in India
With an objective to further develop the market and with increased need and awareness of market participation, Commodity Options trading (on individual commodities, devolving into the underlying commodity futures) was permitted by SEBI on September 28, 2016 whereas Options which expires into direct delivery of physical commodities (options on goods) were also permitted on January 16, 2020. The futures contracts on commodity indices were permitted on June 18, 2019 and on March 24, 2022, options on commodity indices have been permitted by SEBI after specifying product design and risk management framework.
Commodity Markets Ecosystem is majorly comprised of
Stock Exchange, Brokers, Clearing Corporation, Warehouse Service Provider, Quality Testing Companies, Market Participants such as Farmers, Farmer Producers Organisation (FPO), Value Chain Participants (like exporter and importers), Hedgers, Individuals, Corporates, Proprietary traders, etc.
Settlement of Contracts
The commodity futures contracts can be cash or physically settled. In Indian market, all commodities (except Crude Oil and Natural Gas contracts) are physically settled with the delivery.
Trading Volume
During 2022-23, the average daily turnover in Indian commodities market was about Rs.58,000 crore combined for all four stock exchanges. Of which, about 98% of the trading was happening on MCX alone. The futures contracts contributed about 40%, whereas the options contracts represented about 60% of the turnover during 2022-23. Amongst commodity segment, around 70% of the trading volume was contributed by energy segment (crude oil and natural gas), while 23% trading took place in bullion segment, comprised of gold and silver contracts.
Read Articles
View All

Commodity trade: From Ancient Clay Tablets to Modern Electronic Platforms
The commodity trading has witnessed transformative shifts over the centuries. Ancient Mesopotamian clay tablet contracts established the foundation for commodity derivatives. Historical developments, from Japan's Dojima Rice Exchange to Chicago's CBOT, shaped commodity markets. In modern India, trading occurs on electronic platforms of recognized exchanges, namely MCX, NCDEX, NSE and BSE. The Emergence of nation-wide electronic trading facilities offered by national-level exchanges and certain regulatory requirements led to the closure of smaller or commodity specific exchanges. Over a period, the market regulator, (earlier Forward Market Commission and now SEBI) introduced several measures from time to time to deepen and broaden the market.

Introduction of Options Contracts in Commodity Derivatives
SEBI issued guidelines on product design and risk management framework for options in the commodity derivatives market in June 2017. In the Budget Speech for the year 2016-17, the Hon’ble Finance Minister had, inter-alia proposed that “new derivatives products will be developed by SEBI in the Commodity Derivatives Market”. The introduction of new products into the commodity derivatives markets has been the subject of deliberation at various forums, as it is considered conducive for the overall development of the commodity derivatives market, by attracting broad-based and institutional participation, enhancing liquidity, facilitating hedging and bringing more depth to the commodity derivatives market. The issue of new products in the commodity derivatives market was discussed by the commodity derivatives advisory committee (CDAC) and its sub-groups. The recommendations made by the CDAC inter alia, on the subject of introduction of new products was considered by SEBI. Further, in order to allow commodity derivatives exchanges to offer new products, a consultation paper on amendments to the Stock Exchanges and Clearing Corporations (SECC) Regulations was floated for public comments. After public consultation and on the basis of approval accorded by the SEBI Board, necessary amendments to the SECC Regulations were published in the Gazette on May 29, 2017. Accordingly, necessary guidelines were issued on product design and risk management framework for options in the commodity derivatives market in June 2017, which inter alia included the following:- • Underlying of the options contract shall be commodity future which is amongst top five contracts in terms of turnover subject to minimum threshold turnover. • On a pilot basis each exchange was allowed to launch options on futures on only one commodity. • On exercise, options positions shall devolve into underlying futures position. For further details, please see the SEBI circular SEBI/HO/CDMRD/DMP/CIR/P/104 dated September 28, 2016.

Introduction of Options on Commodity Indices
SEBI permitted the launch of options on commodity indices, leading to an expansion of the range of available commodity derivative products. The detailed framework on product design and comprehensive risk management was issued vide circular dated March 24, 2022.

Portfolio Manager - Participation in Commodity Derivatives
In order to promote institutional participation in the Exchange Traded Commodity Derivatives (ETCDs), SEBI has permitted Category III Alternative Investment Funds, Eligible Foreign Entities and Mutual Funds to participate in ETCDs. In furtherance to this objective, SEBI has given its nod for the participation of portfolio managers in ETCDs on behalf of their clients.

Direct Market Access (DMA) to FPIs in ETCDs
In order to promote institutional participation in Exchange Traded Commodity Derivatives (ETCDs) and based on representations received for enabling Direct Market Access (DMA) facility to FPIs in ETCDs and deliberations by Commodity Derivatives Advisory Committee(CDAC) of SEBI, SEBI allowed stock exchanges to extend DMA facility to FPIs for participation in ETCDs subject to certain conditions prescribed vide circular dated September 29, 2022

Goods notified under SCRA, 1956 expanded
Subsequent to the representations received from stock exchanges and due deliberations by the Commodity Derivatives Advisory Committee (CDAC) to enhance the depth of the commodity derivatives market, the earlier list of 91 goods notified under clause (bc) of Section 2 of SCRA vide MoF’s earlier notification dated September 27, 2016 was expanded to 104 commodities vide MoF notification dated March 01, 2024. The revised list now encompasses an additional 13 goods, which include alloys for five metals.

Introduction of Futures on Commodity Indices
Introduction of new commodity derivative products is considered conducive to the overall development of the commodity derivatives market as it helps in attracting broad-based participation, enhances liquidity, facilitates hedging and brings in more depth to the commodity derivatives market. In the Union Budget Speech for the year 2016-17, The Finance Minister announced that new derivatives products will be developed by SEBI in the Commodity Derivatives Market. Pursuant to this, SEBI permitted recognized stock exchanges with commodity derivative segments to introduce futures on commodity indices and issued guidelines for the design of commodity indices and product design for futures on commodity indices.

Framework for Gold Spot Exchange
In the Union Budget 2021-22, the Hon'ble Finance Minister announced the setting up of a Gold Spot Exchange and that SEBI would be the designated regulator for the proposed gold exchanges. Accordingly, SEBI proposed a regulatory framework for the gold exchanges in India and SEBI (Vault Managers) Regulation, 2021 to operationalise the gold exchanges and trading of EGRs in India. The broad specifications for EGR contracts were issued, enabling stock exchanges to introduce diverse denominations. These initiatives aim to enhance transparency and efficiency in India's gold market.

Guidelines with respect to the incentives under the Liquidity Enhancement Scheme (LES) in Commodity Derivatives Contracts
SEBI prescribed guidelines for the Liquidity Enhancement Scheme in commodity derivatives contracts in March 2018, subject to certain conditions stipulated vide April 2014 circular. However, since an exchange in nascent stage of business may not be able to generate profits or have free reserves from business operations, SEBI, vide circular dated July 26, 2019, has exempted such exchanges from above mentioned guidelines and prescribed new guidelines with respect to the incentives under the liquidity enhancement scheme.

Guidelines to Operationalize Options on Goods
SEBI, in consultation with Commodity Derivatives Advisory Committee (CDAC) and vide Circular SEBI/HO/CDMRD/DMP/CIR/P/104 dated September 28, 2016, issued guidelines for trading of options in Commodity Derivatives Market. Initially, ‘Options’ were permitted for trading on only on those commodity futures as underlying, which are traded on exchange platforms with some specific criteria. Thereafter, the government notification dated October 18, 2019, paved the way for introduction of ‘options on Goods’. Accordingly, SEBI vide circular dated January 16, 2020, issued necessary guidelines on product design and risk management framework to operationalize ‘Options on Goods’ in the commodity derivatives market in addition to ‘Options on Commodity Futures’.
Watch Videos
View All

Introduction to Commodity Derivatives Trading
The video gives an Introduction to Commodity Derivatives Trading in India

Evolution of Commodity Derivatives Market in India
Infographic Video - Overview of the Evolution of Commodity Derivatives Market in India
Evolution of Commodities Markets via Numbers
Infographic Video - Evolution of Commodities Markets via Numbers
View Images
View All
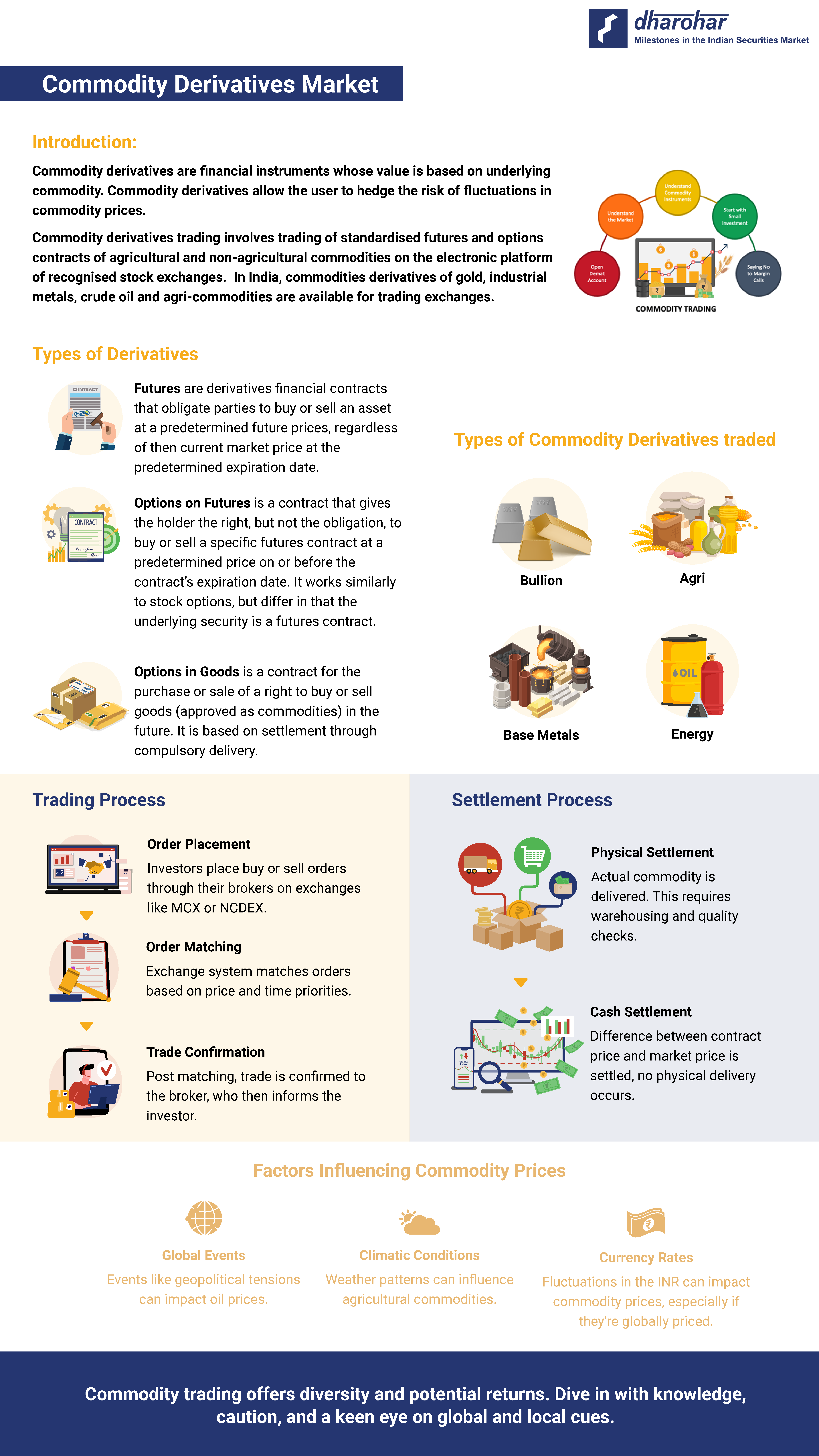
Commodity Derivatives Trading & Settlement in India
Derivates are contracts set between two or more parties, that derive their value from an underlying asset, group of assets, or benchmarks. In India, it encompasses a range of commodities from precious metals to agricultural products.
